What is Gravity?
Gravity is an invisible force between objects and the Earth that pulls objects towards the Earth. This changes from place to place.
What is Gravitational Force?
Gravitational Force is an invisible force of attraction between any two objects in the universe. It is an attraction between objects that have mass. Its value is constant everywhere in the universe. That is G= 6.674×10−11 N⋅m2/kg2
~ Did You Know: Newton discovered Gravity! He also formulated laws regarding it. ( Which we will be discussing later on!)
Solar System Time!~
History of Our Solar System and Force of Gravity.
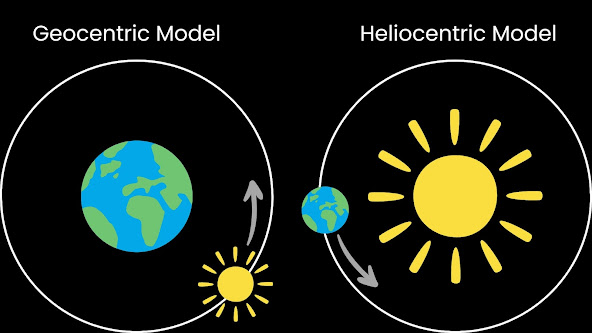
- The first model of our solar system was the Geocentric Model.
- This theory was first stated by Ptolemy.
- In this model the Earth is situated in the centre of the universe.
- Nicolas Copernicus was the first man who declared that Sun was in the centre.
- He proposed the Heliocentric Model, where the Sun is in the centre.
- Then, Tycho Brahe, an astronomer spent his entire life mapping stars without a telescope!
- Now with Tycho's works a new astronomer came, Johannes Kepler.
- He was appointed as the assistant of Tycho, but one year later Tycho died and Kepler stole Tycho's maps to research. (We will talk about him later on!)
- Then came the discovery of telescope, by Galileo Galilei.
- Both Kepler and Galileo believed in the ideas of Copernicus.
Kepler's Laws.
1)The Law of Orbits
The orbit of a planet is an ellipse with the sun as one of the foci.
2)The Law of Areas
The line joining the planet and the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time.
3)The Law of Periods
The cube of semi-major axis of the orbit (r) is proportional to the square of its orbital period (T). [ r³/T² = Constant ]
Newton' Law of Universal Gravitation.
Every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between centres the objects.
Which is F = GMm/r² where,
G is the Constant of Proportionality = 6.674×10−11 N⋅m2/kg2
M is the mass of Object 1
m is the mass of Object 2
m is the mass of Object 2
r is the Distance
F is the Gravitational Force between the Objects.
~He also stated that Gravity travels in the speed of light.
Before we go to the next topic let us all know about mass and weight.
1) Mass ( According to Phys ): It is the measure of Inertia. Mass is Constant.
2) Weight : Weight of an object is the force with which gravity acts on an object. Weight varies from place to place.
So because of this people weigh differently on different planets.
Ex. If in Earth you weighs 45 kg. So in Mars you would weigh 17.2 kg.
------
What is Centripetal Force?
It is a centre seeking force that makes an object to follow a circular path, revolving around a fixed point. The force to always perpendicular to the objects displacement and velocity.
What is Centrifugal force?
It is force that is directed away from the centre in a revolving motion. It is also perpendicular to the displacement of the object but it is in the opposite direction to centripetal force.
Both of these forces are very crucial, and because of them only the Earth is revolving around the earth and is not moving towards the Sun nor moving away from the Sun.
What is free fall?
You would have heard this term "Free Fall" somewhere, but what does it mean? It is a condition were only the gravitational force acts on you.
Now the acceleration provided by Gravity (g) on earth is 9.8 m/s² ( At the Equators).
And that of Moon is 1/6th of Earth's acceleration due to gravity which is 1.62 m/s².
------
Now let us talk about one phenomenon in which gravity plays an important role: Buoyancy.
But before that, we should understand some terms related to it.
1) Pressure: It is the force acting on per unit area. Unit is Pascal (Pa or Nm^-2)
2) Thrust: It is the perpendicular force acting on a body.
3) Density: It is a measurement of how densely molecules of a body are packed together. It is Mass per unit Volume.
3) Some properties of Liquid related to Buoyancy:
- Liquids have pressure and this pressure acts on every direction.
- The deeper you go inside a liquid the larger the pressure.
Now what is Buoyancy?
It is the tendency of a liquid to push you up or to keep you afloat.
Now if the density of water is more than that of the object then the object will float and if the density of water is less that the density of the object then the object will sink.
Last but not the least is the Archimedes Principle.
When an object is immersed in a container, containing water the buoyant force that it feels is exactly equal to the weight of the water it displaces out of the container.
That is,
Buoyant Force = The Weight of Water Displaced
THE END
~Thank You~
------------



Post a Comment